Difference between revisions of "Electronics Basics"
(→ESCs) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== ESCs == | == ESCs == | ||
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
| − | An ESC (Electronic Speed Control) receives a control signal from the reciever that dictates how much power to output to the motor. It then generates a signal of the proper power and sends it to the motor. For brushless motors the ESC will generate a three phase AC signal, and for brushed motors the ESC will generate a constant signal. Click here to learn more about the difference between brushed and brushless ESCs. The ESCs adjust the phase of the output based on the motor rotation, which it measures using the back emf response from the motor. This allows the user to spin the motor at different speeds to control the speed and direction of the robot | + | An ESC (Electronic Speed Control) receives a control signal from the reciever that dictates how much power to output to the motor. It then generates a signal of the proper power and sends it to the motor. For brushless motors the ESC will generate a three phase AC signal, and for brushed motors the ESC will generate a constant signal. [http://www.hooked-on-rc-airplanes.com/brushed-vs-brushless-esc.html| Click here] to learn more about the difference between brushed and brushless ESCs. The ESCs adjust the phase of the output based on the motor rotation, which it measures using the back emf response from the motor. This allows the user to spin the motor at different speeds to control the speed and direction of the robot |
=== Choosing an ESC === | === Choosing an ESC === | ||
ESCs are chosen based on the max current they will experience. Generally the ESC’s rated current should be higher than the motor’s rated current. For example a 30A motor will generally require a 40A ESC to prevent overvoltage. The ESCs will also need a Battery Eliminator Circuit (BEC) to step down the voltage to the receiver. The presence of a BEC will be listed in the ESC’s product specifications. | ESCs are chosen based on the max current they will experience. Generally the ESC’s rated current should be higher than the motor’s rated current. For example a 30A motor will generally require a 40A ESC to prevent overvoltage. The ESCs will also need a Battery Eliminator Circuit (BEC) to step down the voltage to the receiver. The presence of a BEC will be listed in the ESC’s product specifications. | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 5 November 2018
Contents
Overview
Electronics are an important consideration of all Combat bots. Robots without strong electronics can suffer from shorts and over-voltage, which can ruin components and disable the robot. Creating a strong electrical system is crucial to increasing the durability and maximizing the damage output of the robot. Additionally, compact electronics allow the designer to decrease the size and footprint of the robot,
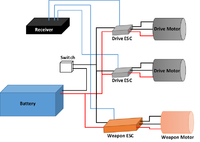
3lb Circuit
The standard 3lb electrical layout consists of a 1000 mAh 11.1 V battery connected to a mechanical switch, which powers 2 drive ESCs and a Weapon ESC. The ESCs are each connected to a receiver and send power to the motors in 3 phases.
Parts List
- 1000mAh 11.1V Battery
- Drive ESCs
- Drive Motors
- Switch
- Receiver
Motors
Motors consist of a rotor (rotating part) and a stator (stationary part). The rotor is made up of an armature that drives the load which is surrounded by magnets and supported by a bearing to reduce friction. The stator is made up of a core surrounded by coils of wire connected to a power source that is used to drive the motor. The stator has a core made up of laminated sheets of metal to reduce energy losses. A commutator is also included in brushed motors to flip the magnetic field as the motor spins.
Brushed vs Brushless
Brushed motors operate by sending current through coils of wire to induce a magnetic field and cause the motor’s permanent magnets to turn. Once the magnets have spun 180°, the current is reversed using a communicator, and the magnets continue to spin another 180° and the process repeats. Brushed motors are more durable than brushless motors, but suffer from less control and slower speeds than brushless motors.
Brushless motors operate using three phase AC current generated by a switching power source or an ESC. The 3 phases of the current are 120 defrees out of phase, meaning that when one line has no current, the other lines have a current at plus and minus cos(120°). These wires are connected in loops around the motor in alternating phases so that at any moment, one wire is pushing the motor forward, one is pulling the motor forward, and the last has no current.
Brushless motor’s have a higher power to weight ratio and higher speed than brushed motors. Battlebots uses brushless motors for its robots due to the control and speeds that they posses. Note that the direction of the motor can be reversed by switching any 2 of the wires.
Inrunner vs Outrunner
Inrunner motors have the permanent magnet rotor inside a ring of electromagnets with the armature connected directly to the rotor. Inrunner motor’s have high rpm and are more efficient than outrunners, but have less torque and weigh more?.
Outrunner motor’s have the permanent magnet rotor outside a core of electromagnets with the armature connected to a plate on the back of the rotor. Outrunner motors provide more torque than inrunners, but suffer from less rpm and a spinning body that can be constricted by wires.
Choosing a Motor
ESCs
Overview
An ESC (Electronic Speed Control) receives a control signal from the reciever that dictates how much power to output to the motor. It then generates a signal of the proper power and sends it to the motor. For brushless motors the ESC will generate a three phase AC signal, and for brushed motors the ESC will generate a constant signal. Click here to learn more about the difference between brushed and brushless ESCs. The ESCs adjust the phase of the output based on the motor rotation, which it measures using the back emf response from the motor. This allows the user to spin the motor at different speeds to control the speed and direction of the robot
Choosing an ESC
ESCs are chosen based on the max current they will experience. Generally the ESC’s rated current should be higher than the motor’s rated current. For example a 30A motor will generally require a 40A ESC to prevent overvoltage. The ESCs will also need a Battery Eliminator Circuit (BEC) to step down the voltage to the receiver. The presence of a BEC will be listed in the ESC’s product specifications.
Batteries
Battlebots uses Lithium Polymer batteries to power our electronics. Lithium polymer batteries are compact rechargeable batteries made using a polymer electrolyte to reduce weight. LiPo batteries have high energy density and low weight, making them perfect for applications with weight restrictions. The 3lb robots use a 1000mAh 3-cell battery which has enough charge to power the robots for their three minute matches.
Safety
Reciever
Depending on the reciever, The trim may need to be adjusted to successfully bind.