Difference between revisions of "Materials Database"
(→AR500 Steel) |
(→AR500 Steel) |
||
| (90 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
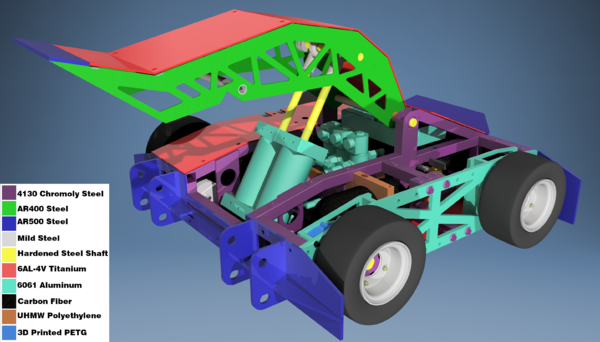
| − | [[File:Duck.png|right|thumb|600px| | + | [[File:Duck.png|right|thumb|600px|Subzero's Materials (250lber)]] |
This is a brief database of useful properties for commonly used materials within battlebots as well as some background information and peoples' experience working with them. Some material properties have not been included but feel free to add anything important. Material properties usually vary slightly for a given material from vendor to vendor so in the majority of cases, trust specs given by the manufacturer or supplier over the specs in this database when they are given. In addition, some of these material properties can vary slightly depending on the data source and also other details such as heat treatment and the kind of sample the material data was acquired from. | This is a brief database of useful properties for commonly used materials within battlebots as well as some background information and peoples' experience working with them. Some material properties have not been included but feel free to add anything important. Material properties usually vary slightly for a given material from vendor to vendor so in the majority of cases, trust specs given by the manufacturer or supplier over the specs in this database when they are given. In addition, some of these material properties can vary slightly depending on the data source and also other details such as heat treatment and the kind of sample the material data was acquired from. | ||
== Steels == | == Steels == | ||
| − | === AR500 Steel === | + | Steels are strong, dense, iron-carbon alloys which come in a variety of material compositions and treatment standards. A variety of major and minor alloying elements are added to improve certain material properties, including strength, toughness, corrosion resistance, or machinability. When selecting a grade of steel to use for your robot, consider how the material properties of the steel address the design requirements. Listed below are some more common grades of steel: |
| + | |||
| + | === Abrasion-Resistant (AR) Steel === | ||
| + | "AR" Steel, or "Abrasion Resistant" Steel is a high-strength, low carbon hardened alloy designed to resist wear and stress. The "grade" of the abrasion-resistant steel correlates to the Brinell hardness rating. | ||
| + | ==== AR500 Steel ==== | ||
{| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 26: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Brinell Hardness | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| − | | 450 HB | + | | 450 HB |
|- | |- | ||
| Rockwell Hardness | | Rockwell Hardness | ||
| − | | | + | | C47-48 |
|- | |- | ||
| Elongation at Break | | Elongation at Break | ||
| 12% | | 12% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact (V-notch) | ||
| + | | 24.4J | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Familiar Sellers | | Familiar Sellers | ||
| Line 47: | Line 55: | ||
*Anecdotal experience from builders says that AR500 typically bends before it fractures | *Anecdotal experience from builders says that AR500 typically bends before it fractures | ||
*Will rust over time when wet or exposed to air | *Will rust over time when wet or exposed to air | ||
| + | *Important to select a supplier which gives you specifications and complies with specification codes. AR steels are not tightly regulated so the actual hardness and depth of hardening (completely through-hardened vs surface hardened) may vary by supplier. | ||
| + | **Technically supposed to be through hardened but many sketchier suppliers will sell AR500 that is effectively only surface hardened (up to 1/8" depth from surface according to Seth from JustCuzRobotics/BloodSport) with decreasing hardness with depth and a soft core. This doesn't matter much for thinner parts 1/4" or thinner but matters alot for thicker parts. | ||
| − | ===AR400 Steel=== | + | ====AR400 Steel==== |
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Type | ||
| + | | Carbon Steel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Modulus of Elasticity | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shear Modulus | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Poisson's Ratio | ||
| + | | XX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Density | ||
| + | | XX lb/in^3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Ultimate Tensile Strength | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Tensile Yield Strength | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | ||
| + | | XX ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | XX J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact (V-notch) | ||
| + | | ~XX J | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| + | | XXXX HB | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Rockwell Hardness | ||
| + | | CXX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Elongation at Break | ||
| + | | ~XX% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Familiar Sellers | ||
| + | | McMaster, Online Metals | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | ===S7 Tool Steel (at 54 HRC)=== | + | ===Tool Steel=== |
| + | Unlike abrasion-resistant or carbon steels, tool steels are specialized grades of steel used primarily for tool production and cutting bits. | ||
| + | Added alloying elements such as Cr, V, Co, W, or Mo are added to greatly increase the strength and wear resistance of the steel, but tool steels tend to be more expensive than standard carbon steels. | ||
| + | ====S7 Tool Steel (at 54 HRC)==== | ||
{| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 80: | Line 145: | ||
| Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | | Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | ||
| 50.0 ksi-in½ | | 50.0 ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | 9.42 J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact (V-notch) | ||
| + | | 16.3 J | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Brinell Hardness | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| Line 95: | Line 168: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | *Shock resisting tool steel that has high strength and high toughness | + | *Shock resisting tool steel that has high strength and high impact toughness |
*Usually used in weapons but has been used by some NHRL builders for shafts but with hardnesses much lower than 54 HRC | *Usually used in weapons but has been used by some NHRL builders for shafts but with hardnesses much lower than 54 HRC | ||
*Is machined in its annealed form and then heat treated, quenched, and tempered to exactly 54 HRC which is a value recommended by the Riobotz Combot Tutorial pg 59-60. | *Is machined in its annealed form and then heat treated, quenched, and tempered to exactly 54 HRC which is a value recommended by the Riobotz Combot Tutorial pg 59-60. | ||
| Line 101: | Line 174: | ||
*Anecdotal experience from other builders shows it fails through fracture before bending | *Anecdotal experience from other builders shows it fails through fracture before bending | ||
*Considered to be less tough than AR500 and is commonly used when the higher hardness (C54 vs C48) is desired like for weapon teeth | *Considered to be less tough than AR500 and is commonly used when the higher hardness (C54 vs C48) is desired like for weapon teeth | ||
| + | *Extra important to avoid sharp internal corners and stress concentrations to prevent cracks from forming | ||
| − | ===AISI 4340 | + | ===AISI Alloy Steels=== |
| + | (description here) | ||
| + | ====AISI 4340 (43 HRC)==== | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Type | ||
| + | | Carbon Steel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Modulus of Elasticity | ||
| + | | 29,732 ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shear Modulus | ||
| + | | 11900 ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Poisson's Ratio | ||
| + | | 0.29 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Density | ||
| + | | 0.283 lb/in^3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Ultimate Tensile Strength | ||
| + | | 210.0 ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Tensile Yield Strength | ||
| + | | 194.9 ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | ||
| + | | 80.1 ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | 24.38 J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact (V-notch) | ||
| + | | ~19 J | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| + | | 402 HB | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Rockwell Hardness | ||
| + | | C43 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Elongation at Break | ||
| + | | ~9.6% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Familiar Sellers | ||
| + | | McMaster, Online Metals | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | ===AISI 4140 | + | *Ultra high strength steel that is machined in its annealed state and is heat treated by quenching and tempering it to a desired hardness. |
| + | *Riobotz's recommended hardness for shafts is 40-43 HRC which will allow it to fail by bending before breaking | ||
| + | *Is often used by some builders for other parts such as beaterbars at higher hardnesses | ||
| + | *Relatively expensive | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====AISI 4140 (-- HRC)==== | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Type | ||
| + | | Carbon Steel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Modulus of Elasticity | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shear Modulus | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Poisson's Ratio | ||
| + | | XX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Density | ||
| + | | XX lb/in^3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Ultimate Tensile Strength | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Tensile Yield Strength | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | ||
| + | | XX ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | XX J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact (V-notch) | ||
| + | | ~XX J | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| + | | XXXX HB | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Rockwell Hardness | ||
| + | | CXX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Elongation at Break | ||
| + | | ~XX% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Familiar Sellers | ||
| + | | McMaster, Online Metals | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
==Aluminum Alloys== | ==Aluminum Alloys== | ||
| Line 138: | Line 323: | ||
| Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | | Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | ||
| 26.4 ksi-in½ | | 26.4 ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | 7.88 J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | ||
| + | | 21.7 J | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Brinell Hardness | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| Line 194: | Line 387: | ||
| Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | | Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | ||
| 22.8 ksi-in½ | | 22.8 ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | 5.87 J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | ||
| + | | 5.4 J | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Brinell Hardness | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| Line 217: | Line 418: | ||
*Past and anecdotal experience notes that it tends to fracture before it bends as it's more brittle than 6061 | *Past and anecdotal experience notes that it tends to fracture before it bends as it's more brittle than 6061 | ||
*Some builders recommend avoiding using it as armor or for parts that take direct hits due to fracture risk | *Some builders recommend avoiding using it as armor or for parts that take direct hits due to fracture risk | ||
| − | *Relatively easy to machine | + | *Relatively easy to machine |
| + | *More expensive than 6061-T6 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Aluminum 5052-H32 === | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Type | ||
| + | | Aluminum Alloy | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Modulus of Elasticity | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shear Modulus | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Poisson's Ratio | ||
| + | | XX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Density | ||
| + | | XX lb/in^3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Ultimate Tensile Strength | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Tensile Yield Strength | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | ||
| + | | XX ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | XX J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | ||
| + | | XX J | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| + | | XX HB | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Rockwell Hardness | ||
| + | | BXX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Elongation at Break | ||
| + | | XX% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Machinability (Vs. 1112 Steel) | ||
| + | | XX% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Familiar Sellers | ||
| + | | McMaster Carr, Midwest Steel Supply, SendCutSend | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Material Description: | ||
| + | * | ||
===Aluminum 2024-T6=== | ===Aluminum 2024-T6=== | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width: 500px;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Type | ||
| + | | Aluminum Alloy | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Modulus of Elasticity | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shear Modulus | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Poisson's Ratio | ||
| + | | 0.XX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Density | ||
| + | | XX lb/in^3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Ultimate Tensile Strength | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Tensile Yield Strength | ||
| + | | XX ksi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | ||
| + | | XX ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | XX J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | ||
| + | | XX J | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| + | | XX HB | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Rockwell Hardness | ||
| + | | BXX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Elongation at Break | ||
| + | | XX% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Machinability (Vs. 1112 Steel) | ||
| + | | XX% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Familiar Sellers | ||
| + | | McMaster Carr, Midwest Steel Supply, SendCutSend | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Material Description: | ||
| + | * | ||
==Other Metal Alloys== | ==Other Metal Alloys== | ||
| Line 252: | Line 570: | ||
| Fracture Toughness (Annealed Plate) | | Fracture Toughness (Annealed Plate) | ||
| 67.9 ksi-in½ | | 67.9 ksi-in½ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Calculated Toughness | ||
| + | | 31.5 J/in^2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | ||
| + | | 17 J | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Brinell Hardness | | Brinell Hardness | ||
| Line 272: | Line 598: | ||
Material Description: | Material Description: | ||
*Very high strength and high toughness metal alloy | *Very high strength and high toughness metal alloy | ||
| − | *Denser than aluminum but less dense than steel | + | *Denser than aluminum but less dense than steel. May destroy tools if you're not careful |
*Typically sold and used in its annealed state for high toughness. No heat treatment needed. | *Typically sold and used in its annealed state for high toughness. No heat treatment needed. | ||
*Typically used for armor, structural plates, sometimes weapons, it's pretty versatile material overall | *Typically used for armor, structural plates, sometimes weapons, it's pretty versatile material overall | ||
| − | *Very expensive | + | *Known to fail in bending before failing in fracture |
| + | *Very expensive, more so than most steels and aluminum alloys | ||
*Very difficult to machine or drill due to work hardening properties | *Very difficult to machine or drill due to work hardening properties | ||
*In some cases, outsourcing to SendCutSend might be financial preferable to buying Ti stock so discuss with your PM | *In some cases, outsourcing to SendCutSend might be financial preferable to buying Ti stock so discuss with your PM | ||
==Plastics and Polymers== | ==Plastics and Polymers== | ||
| + | Plastics and other polymerized materials are significantly less dense than metals, and are generally more machinable or formable. | ||
| + | |||
===Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight-Polyethylene (UHMW)=== | ===Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight-Polyethylene (UHMW)=== | ||
===High-Density-Polyethylene (HDPE)=== | ===High-Density-Polyethylene (HDPE)=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Polycarbonate=== | ||
===Carbon Fiber=== | ===Carbon Fiber=== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Polylactide Plastic (PLA)=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)=== | ||
| + | |||
== Sources == | == Sources == | ||
| − | *AR500 Steel: SendCutSend | + | *AR500 Steel: |
| − | *Al 6061-T6: SendCutSend | + | **SendCutSend: https://sendcutsend.com/materials/ar500/ |
| − | *Al 7075-T6: SendCutSend | + | **Steel Warehouse: https://www.steelwarehouse.com/ar500/ |
| − | *Ti-6Al-4V: SendCutSend | + | **Team Caustic Creations: https://www.arrow.com/en/research-and-events/articles/battlebot-episode-2 |
| + | |||
| + | *AR400 Steel: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | *S7 Tool Steel: | ||
| + | **Riobotz Combot Tutorial (Pg. 82): https://www.riobotz.com/riobotz-combot-tutorial | ||
| + | **Ansys Granta Edupack (Not 54 HRC but some properties are close enough): https://drive.google.com/file/d/1aNH_X-EIR3ae4Uacl5s5DzcEWLtHAgMG/view?usp=sharing | ||
| + | **Team Caustic Creations: https://www.arrow.com/en/research-and-events/articles/battlebot-episode-2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *AISI 4340 Steel (43 HRC): | ||
| + | **Riobotz Combot Tutorial | ||
| + | **'The quantitative relationship between fracture toughness and impact toughness in high-strength steels': https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331525402_The_quantitative_relationship_between_fracture_toughness_and_impact_toughness_in_high-strength_steels | ||
| + | |||
| + | *AISI 4140 Steel: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Al 6061-T6: | ||
| + | **SendCutSend: https://sendcutsend.com/materials/6061-aluminum/ | ||
| + | **Matweb: https://asm.matweb.com/search/SpecificMaterial.asp?bassnum=ma6061t6 | ||
| + | **Machining Doctor: https://www.machiningdoctor.com/mds/?matId=3850 (Machinability) | ||
| + | **Team Caustic Creations: https://www.arrow.com/en/research-and-events/articles/battlebot-episode-2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Al 7075-T6: | ||
| + | **SendCutSend: https://sendcutsend.com/materials/7075-aluminum/ | ||
| + | **Matweb: https://asm.matweb.com/search/SpecificMaterial.asp?bassnum=ma7075t6 | ||
| + | **Machining Doctor: https://www.machiningdoctor.com/mds/?matId=3970 (Machinability) | ||
| + | **Team Caustic Creations: https://www.arrow.com/en/research-and-events/articles/battlebot-episode-2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Al 5052-H32: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Al 2024-T6: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ti-6Al-4V: | ||
| + | **SendCutSend: https://sendcutsend.com/materials/titanium/ | ||
| + | **Matweb: https://asm.matweb.com/search/SpecificMaterial.asp?bassnum=mtp641 | ||
| + | **Machining Doctor: https://www.machiningdoctor.com/machinability/titanium/ (Machinability) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *UHMW: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| − | == | + | *HDPE: |
| − | * | + | **source |
| + | |||
| + | *Polycarbonate: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Carbon Fiber: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | *ABS: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | *PLA: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | *TPU: | ||
| + | **source | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes == | ||
| + | *The charpy impact data provided by Team Caustic Creations was "quick and dirty" and was hard to verify | ||
| + | **They didn't specify how they got the data and where from | ||
| + | **Their value for Ti-6Al-4V was off from the Matweb data page so take it with a grain of salt | ||
| + | **Charpy impact data is pretty hard to find. It might be worth it for RoboJackets to our own Charpy impact tests | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The Plastics and Polymers section does not distinguish the material property differences between machined stock pieces and extruded 3D prints. Because of the layer-by-layer extrusion of 3D printers, it is vital to note that the material strength is directionally dependent, and depends on the infill style and percentage infill. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:50, 12 April 2023
This is a brief database of useful properties for commonly used materials within battlebots as well as some background information and peoples' experience working with them. Some material properties have not been included but feel free to add anything important. Material properties usually vary slightly for a given material from vendor to vendor so in the majority of cases, trust specs given by the manufacturer or supplier over the specs in this database when they are given. In addition, some of these material properties can vary slightly depending on the data source and also other details such as heat treatment and the kind of sample the material data was acquired from.
Steels
Steels are strong, dense, iron-carbon alloys which come in a variety of material compositions and treatment standards. A variety of major and minor alloying elements are added to improve certain material properties, including strength, toughness, corrosion resistance, or machinability. When selecting a grade of steel to use for your robot, consider how the material properties of the steel address the design requirements. Listed below are some more common grades of steel:
Abrasion-Resistant (AR) Steel
"AR" Steel, or "Abrasion Resistant" Steel is a high-strength, low carbon hardened alloy designed to resist wear and stress. The "grade" of the abrasion-resistant steel correlates to the Brinell hardness rating.
AR500 Steel
| Type | Carbon Steel |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 30,000 ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.29 |
| Density | 0.29 lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 225 ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 200 ksi |
| Brinell Hardness | 450 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | C47-48 |
| Elongation at Break | 12% |
| Charpy Impact (V-notch) | 24.4J |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster Carr, MakeItRingTargets, Alro Steel, SendCutSend |
Material Description:
- High strength, high hardness, abrasion resistant steel used in body armor and shooting targets
- Generally considered to be tougher than S7 tool steel but has lower hardness
- Hardened steel is very difficult to machine, is typically only used for Waterjet parts
- No further heat treatment needed
- Typically used for weapons and wedges due to it's high strength, toughness, and relatively high hardness
- Used more commonly as armor in higher weight classes
- Anecdotal experience from builders says that AR500 typically bends before it fractures
- Will rust over time when wet or exposed to air
- Important to select a supplier which gives you specifications and complies with specification codes. AR steels are not tightly regulated so the actual hardness and depth of hardening (completely through-hardened vs surface hardened) may vary by supplier.
- Technically supposed to be through hardened but many sketchier suppliers will sell AR500 that is effectively only surface hardened (up to 1/8" depth from surface according to Seth from JustCuzRobotics/BloodSport) with decreasing hardness with depth and a soft core. This doesn't matter much for thinner parts 1/4" or thinner but matters alot for thicker parts.
AR400 Steel
| Type | Carbon Steel |
| Modulus of Elasticity | XX ksi |
| Shear Modulus | XX ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | XX |
| Density | XX lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | XX ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | XX ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | XX ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | XX J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact (V-notch) | ~XX J |
| Brinell Hardness | XXXX HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | CXX |
| Elongation at Break | ~XX% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster, Online Metals |
Tool Steel
Unlike abrasion-resistant or carbon steels, tool steels are specialized grades of steel used primarily for tool production and cutting bits. Added alloying elements such as Cr, V, Co, W, or Mo are added to greatly increase the strength and wear resistance of the steel, but tool steels tend to be more expensive than standard carbon steels.
S7 Tool Steel (at 54 HRC)
| Type | Carbon Steel |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 30,000 ksi |
| Shear Modulus | 11900 ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.29 |
| Density | 0.282 lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 284.9 ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 220.4 ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | 50.0 ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | 9.42 J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact (V-notch) | 16.3 J |
| Brinell Hardness | 543 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | C54 |
| Elongation at Break | 6.5% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster Carr, OnlineMetals |
- Shock resisting tool steel that has high strength and high impact toughness
- Usually used in weapons but has been used by some NHRL builders for shafts but with hardnesses much lower than 54 HRC
- Is machined in its annealed form and then heat treated, quenched, and tempered to exactly 54 HRC which is a value recommended by the Riobotz Combot Tutorial pg 59-60.
- Ray Billings, builder of Tombstone, also endorses exactly 54 HRC for S7
- Anecdotal experience from other builders shows it fails through fracture before bending
- Considered to be less tough than AR500 and is commonly used when the higher hardness (C54 vs C48) is desired like for weapon teeth
- Extra important to avoid sharp internal corners and stress concentrations to prevent cracks from forming
AISI Alloy Steels
(description here)
AISI 4340 (43 HRC)
| Type | Carbon Steel |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 29,732 ksi |
| Shear Modulus | 11900 ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.29 |
| Density | 0.283 lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 210.0 ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 194.9 ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | 80.1 ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | 24.38 J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact (V-notch) | ~19 J |
| Brinell Hardness | 402 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | C43 |
| Elongation at Break | ~9.6% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster, Online Metals |
- Ultra high strength steel that is machined in its annealed state and is heat treated by quenching and tempering it to a desired hardness.
- Riobotz's recommended hardness for shafts is 40-43 HRC which will allow it to fail by bending before breaking
- Is often used by some builders for other parts such as beaterbars at higher hardnesses
- Relatively expensive
AISI 4140 (-- HRC)
| Type | Carbon Steel |
| Modulus of Elasticity | XX ksi |
| Shear Modulus | XX ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | XX |
| Density | XX lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | XX ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | XX ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (Riobotz Sample) | XX ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | XX J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact (V-notch) | ~XX J |
| Brinell Hardness | XXXX HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | CXX |
| Elongation at Break | ~XX% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster, Online Metals |
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum 6061-T6
| Type | Aluminum Alloy |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 10,000 ksi |
| Shear Modulus | 3800 ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.33 |
| Density | 0.0984 lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 45 ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 39 ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | 26.4 ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | 7.88 J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | 21.7 J |
| Brinell Hardness | 93 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | B52 |
| Elongation at Break | 10% |
| Machinability (Vs. 1112 Steel) | 270% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster Carr, Midwest Steel Supply, SendCutSend |
Material Description:
- Lightweight aluminum alloy that comes already pre-heat-treated T6 temper which gives it its strength
- Beware of tempers T4 and O which are weaker than 6061-T6
- Typically used for frame rails, plates, pulleys, and armor for some bots
- Tends to fail in bending before fracturing
- Tends to "ablate" and may take gashes when hit directly by weapons
- Easy to machine and relatively cheap
Aluminum 7075-T6
| Type | Aluminum Alloy |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 10,000 ksi |
| Shear Modulus | 3800 ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.32 |
| Density | 0.102 lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 81 ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 69 ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | 22.8 ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | 5.87 J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | 5.4 J |
| Brinell Hardness | 150 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | B87 |
| Elongation at Break | 7.9% |
| Machinability (Vs. 1112 Steel) | 170% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster Carr, Midwest Steel Supply, SendCutSend |
Material Description:
- Aerospace grade aluminum alloy which is much stronger and harder than 6061-T6
- Pre-heat-treated to T6 temper
- Past and anecdotal experience notes that it tends to fracture before it bends as it's more brittle than 6061
- Some builders recommend avoiding using it as armor or for parts that take direct hits due to fracture risk
- Relatively easy to machine
- More expensive than 6061-T6
Aluminum 5052-H32
| Type | Aluminum Alloy |
| Modulus of Elasticity | XX ksi |
| Shear Modulus | XX ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | XX |
| Density | XX lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | XX ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | XX ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | XX ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | XX J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | XX J |
| Brinell Hardness | XX HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | BXX |
| Elongation at Break | XX% |
| Machinability (Vs. 1112 Steel) | XX% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster Carr, Midwest Steel Supply, SendCutSend |
Material Description:
Aluminum 2024-T6
| Type | Aluminum Alloy |
| Modulus of Elasticity | XX ksi |
| Shear Modulus | XX ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.XX |
| Density | XX lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | XX ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | XX ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (T-L dir) | XX ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | XX J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | XX J |
| Brinell Hardness | XX HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | BXX |
| Elongation at Break | XX% |
| Machinability (Vs. 1112 Steel) | XX% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster Carr, Midwest Steel Supply, SendCutSend |
Material Description:
Other Metal Alloys
Grade 5 Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V)
| Type | Titanium Alloy |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 16510 ksi |
| Shear Modulus | 5800 ksi |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.32 |
| Density | 0.160 lb/in^3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 138-150 ksi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 128-140 ksi |
| Fracture Toughness (Annealed Plate) | 67.9 ksi-in½ |
| Calculated Toughness | 31.5 J/in^2 |
| Charpy Impact Test (V-notch) | 17 J |
| Brinell Hardness | 310 HB |
| Rockwell Hardness | C34 |
| Elongation at Break | 6.7% |
| Machinability (Vs. 1112 Steel) | 20% |
| Familiar Sellers | McMaster Carr, SendCutSend, TMS Titanium |
Material Description:
- Very high strength and high toughness metal alloy
- Denser than aluminum but less dense than steel. May destroy tools if you're not careful
- Typically sold and used in its annealed state for high toughness. No heat treatment needed.
- Typically used for armor, structural plates, sometimes weapons, it's pretty versatile material overall
- Known to fail in bending before failing in fracture
- Very expensive, more so than most steels and aluminum alloys
- Very difficult to machine or drill due to work hardening properties
- In some cases, outsourcing to SendCutSend might be financial preferable to buying Ti stock so discuss with your PM
Plastics and Polymers
Plastics and other polymerized materials are significantly less dense than metals, and are generally more machinable or formable.
Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight-Polyethylene (UHMW)
High-Density-Polyethylene (HDPE)
Polycarbonate
Carbon Fiber
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Polylactide Plastic (PLA)
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Sources
- AR500 Steel:
- SendCutSend: https://sendcutsend.com/materials/ar500/
- Steel Warehouse: https://www.steelwarehouse.com/ar500/
- Team Caustic Creations: https://www.arrow.com/en/research-and-events/articles/battlebot-episode-2
- AR400 Steel:
- source
- S7 Tool Steel:
- Riobotz Combot Tutorial (Pg. 82): https://www.riobotz.com/riobotz-combot-tutorial
- Ansys Granta Edupack (Not 54 HRC but some properties are close enough): https://drive.google.com/file/d/1aNH_X-EIR3ae4Uacl5s5DzcEWLtHAgMG/view?usp=sharing
- Team Caustic Creations: https://www.arrow.com/en/research-and-events/articles/battlebot-episode-2
- AISI 4340 Steel (43 HRC):
- Riobotz Combot Tutorial
- 'The quantitative relationship between fracture toughness and impact toughness in high-strength steels': https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331525402_The_quantitative_relationship_between_fracture_toughness_and_impact_toughness_in_high-strength_steels
- AISI 4140 Steel:
- source
- Al 6061-T6:
- SendCutSend: https://sendcutsend.com/materials/6061-aluminum/
- Matweb: https://asm.matweb.com/search/SpecificMaterial.asp?bassnum=ma6061t6
- Machining Doctor: https://www.machiningdoctor.com/mds/?matId=3850 (Machinability)
- Team Caustic Creations: https://www.arrow.com/en/research-and-events/articles/battlebot-episode-2
- Al 7075-T6:
- SendCutSend: https://sendcutsend.com/materials/7075-aluminum/
- Matweb: https://asm.matweb.com/search/SpecificMaterial.asp?bassnum=ma7075t6
- Machining Doctor: https://www.machiningdoctor.com/mds/?matId=3970 (Machinability)
- Team Caustic Creations: https://www.arrow.com/en/research-and-events/articles/battlebot-episode-2
- Al 5052-H32:
- source
- Al 2024-T6:
- source
- Ti-6Al-4V:
- SendCutSend: https://sendcutsend.com/materials/titanium/
- Matweb: https://asm.matweb.com/search/SpecificMaterial.asp?bassnum=mtp641
- Machining Doctor: https://www.machiningdoctor.com/machinability/titanium/ (Machinability)
- UHMW:
- source
- HDPE:
- source
- Polycarbonate:
- source
- Carbon Fiber:
- source
- ABS:
- source
- PLA:
- source
- TPU:
- source
Notes
- The charpy impact data provided by Team Caustic Creations was "quick and dirty" and was hard to verify
- They didn't specify how they got the data and where from
- Their value for Ti-6Al-4V was off from the Matweb data page so take it with a grain of salt
- Charpy impact data is pretty hard to find. It might be worth it for RoboJackets to our own Charpy impact tests
- The Plastics and Polymers section does not distinguish the material property differences between machined stock pieces and extruded 3D prints. Because of the layer-by-layer extrusion of 3D printers, it is vital to note that the material strength is directionally dependent, and depends on the infill style and percentage infill.