Difference between revisions of "Maori Design Guide"
Tjackson86 (talk | contribs) (→Drive) |
Tjackson86 (talk | contribs) (→Overview) |
||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
==== Overview ==== | ==== Overview ==== | ||
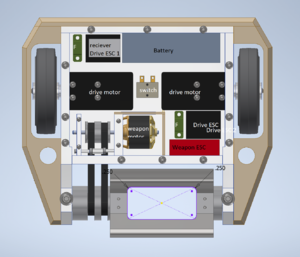
| − | [[File:topdownmaori.png|right|thumb| | + | [[File:topdownmaori.png|right|thumb|300px|Maori Electronics Layout]] |
Maori uses a single battery that powers three parallel circuits, two of which are for drive. There are two 100 A fuses: one for the weapon, the other in series with the two drive circuits. | Maori uses a single battery that powers three parallel circuits, two of which are for drive. There are two 100 A fuses: one for the weapon, the other in series with the two drive circuits. | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 11 April 2020
Contents
Introduction
test
Design Basics
Chassis
Overview
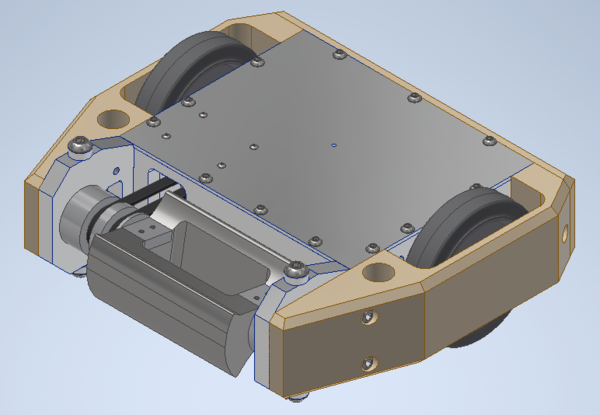
Maori's chassis consists of six parts: A top, bottom, front, and back plate as well as two side plates. All of these components are made from 6061 Aluminum. The side plates provide thicker support towards the weapon, while allowing skids to be inserted. Maori's drive modules also fit into the side plates. The front plate allows for belt access between the interior of the robot and the weapon pulley. It also fits into the side plates The bottom and top plates provide slots for interior plastic guards and bolt into the rest of the chassis.
Design Decisions
Overall, the chassis of our drum type spinner robots have always focused on durability and survivability. We use thicker aluminum plates that slot into each other, along with steel bolts to ensure the base structure of our robot is strong. No real surprises here.
Side Plates (0.5"): Slightly thicker towards the front, along with a slightly flared and rounded profile. Drum spinners run the risk of being ripped open by other robots if the interface between the weapon and chassis is not well put together. To account for this, the front of Maori is a bit thicker than the rest of the side plate (0.625" vs 0.5"). The roundedness to the head/lack of corners is to reduce the number of places where a horizontal spinner would be able to get a good hit on that support portion of the side plates. Cut-outs on the side plates allow for access to the tensioning system for the belt once the armor is removed. The side plates also have weight saving cut outs, and slight pockets that let the drive modules slot in nicely.
Front Plate (0.5"): Standard plate with a cut-out for the belt. Pocketing here gives a bit more room for electronics, while still providing structural support. Slots into side plates.
Back Plate (0.375"): Slightly thinner than the rest of the main chassis plates, but has general weight saving cut-outs. The general idea is that this plate will be slightly thinner as it should not be hit extensively during a fight. Armor also helps with this.
Top/Bottom Plate (0.125"): Maybe slightly too thin, but seemed to hold up well during assembly and testing. Provides holes that allow the tensioning system to bolt into something, while also providing some slots for internal plastic guards.
- Notes/Helpful Advice
- test
Armor
Overview
Maori's armor is composed of three HDPE components. This consists of two side armor blocks and a plate mounted to the back.
Design Decisions
test
- Notes/Helpful Advice
- test
Drive
Overview
The drive assembly is a robust one: An outrunner motor adapted to fit into a Bane Bots gearbox. A multi-piece hub and spacer set, along with a bearing pressed into the side plate allow for proper function.
Design Decisions
test
Calculations
test
- Notes/Helpful Advice
- test
Weapon
Overview
Maori's weapon system consists of a steel drum to cause damage to opponents and two aluminum hubs to interface the weapon with the chassis. The drum is constrained to the hubs with bolts perpendicular to the axis of rotation to minimize loosening caused by vibration. The fork shape of the hubs compromises ease of machining with functionality.
Design Decisions
Beater Bar
- Material: S7 Tool Steel
- Profile: prioritized compatibility for EDM
- constant cross-section along the axis of rotation
- rotationally symmetric for 180 degrees to avoid vibration induced by skewed center of mass
- flats on teeth for clamping when milling out interior profile
- Issues:
- rotationally symmetric profile reduced the "reach" of the weapon, making it hard to deal damage to test specimens
- actual performance in competition cannot be verified
Hubs
- Material: Aluminum 6061-T6
- machined in house, so ease of machining outweighed material selection
- the brunt of forces are received by the beater bar and chassis, this material selection allows deformation of hubs before the beater bar and chassis, which took longer to machine
- Shape:
- fork-shaped puzzle fit with beater bar, constraining axial and radial motion (theoretically could stay together without bolts >:) )
- dual belt slot to effectively halve load on belts
- rotationally symmetric for 180 degrees to avoid skewing the center of mass of the weapon assembly
Calculations
test
- Notes/Helpful Advice
- test
Electronics
Overview
Maori uses a single battery that powers three parallel circuits, two of which are for drive. There are two 100 A fuses: one for the weapon, the other in series with the two drive circuits.
Here is a list of components: - Turnigy 5000 mAh 6S 25C Lipo pack - FrSky X8R 8-channel 2.4ghz reciever - 2 Racerstar 120A ESC rated for 2-6S (drive ESCs) - Scorpion Tribunis 06-120A SBEC (weapon ESC) - 2 Propdrive v2 4238 750KV brushless outrunner motor rated for 80A and 2-4S - Scorpion SII-4025-440KV - 2 Blue Sea AMI/MIDI 100A fuses - Team Whyachi MS-05 Switch
Drive
Calculations for motivating our decisions can be found here: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1scdVNzY6Q3a9BCemg0K2he29hvwmrmOmIFCIPTrqUPA/edit?usp=sharing
Weapon
test
- Notes/Helpful Advice
- test